How to design the start of conversation?
- Getting Started
- Bot Building
- Smart Agent Chat
- Conversation Design
-
Developer Guides
Code Step Integration Static Step Integration Shopify Integration SETU Integration Exotel Integration CIBIL integration Freshdesk KMS Integration PayU Integration Zendesk Guide Integration Twilio Integration Razorpay Integration LeadSquared Integration USU(Unymira) Integration Helo(VivaConnect) Integration Salesforce KMS Integration Stripe Integration PayPal Integration CleverTap Integration Fynd Integration HubSpot Integration Magento Integration WooCommerce Integration Microsoft Dynamics 365 Integration
- Deployment
- External Agent Tool Setup
- Analytics & Reporting
- Notifications
- Commerce Plus
- Troubleshooting Guides
- Release Notes
Words make up a conversation.
And along with words, you also have access to a set of UI elements to make your conversation more engaging. This section aims to give you a complete set of practices and tips that’ll help you craft the conversation!
Bot replies should be crafted keeping all possible input ways in mind. Content should feel all-natural and not disjointed. This section lists the various ways a conversation can be initiated with a bot and the most effective way to design chat initiation.
Menu
- The menu is the list of items shown to the user when they begin the conversation. It’s a guide to help them understand what the bot can do for them and is a great point to start designing your user journey as well.
- The menu is the safest way to start - List all the tasks (isolated items that the bot can do for the user). Examples: Fetching a Bill, Emailing an account statement, Reporting an issue
- Don't get confused between a usecase and a menu item - Usecase is a bigger umbrella than a menu item (The smallest unit of a usecase is a task).
- Create categories for the menu. We recommend that only 3-4 are shown on the UI and then View More.
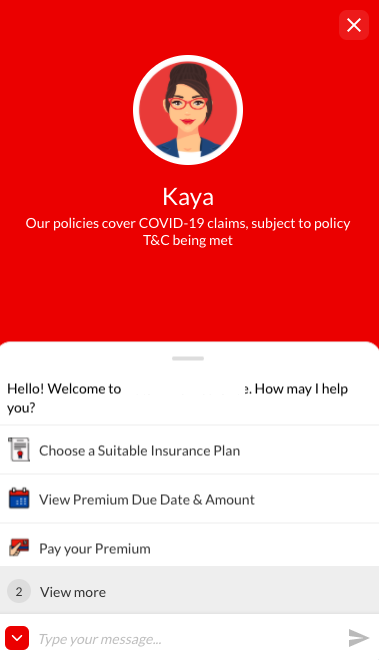
Freeform
- List straightforward variations which will lead to that particular task. Example: I have a complaint should lead to - Have a complaint task.
- List other variations which could lead to that particular task. Example: My package is late should also lead to - Have a complaint task. This should be handled in a separate step.
- We can follow the user message Guidelines for having a clear picture of writing these variations.
- One way to guide users who prefer typing in freeform would be the AutoComplete feature on the Haptik platform. You can customize the option that appears within the AutoComplete window by flagging it in the Conversation Studio. Here’s the documentation to help you enable it on your IVA.

Bot Prompts
Bot prompts are 'notifications' sent to users to draw their attention to the bot’s location and help them understand what the bot can do for them. This is explained in detail below.
- Make sure the button of the prompt leads to the desired step organically. Example: If your bot prompt CTA says “Find a plan”, don't immediately ask the user to enter their details in the text message. Ease the user into the conversation by presenting the plan options and then asking for their details. These small touches will result in conversions.
- Don't have misleading content on the prompt. Avoid using it as advertising real estate for your brand. Make sure the bot’s intentions are clarified at the face value of the prompt.
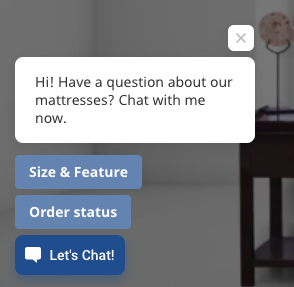
- You can customize several aspects of prompts including the pages they appear on, the delay after which they appear, how they work for repeat users, and so on. Read more about it in our documentation here.
- At the very least, we recommend adding the following bot prompts:
Introductory prompts: Mostly set on the homepage of the website or app, these prompts are a friendly way to draw attention to the bot. Example: Page: On the Home Page Prompt: Hi! I'm Zuri, the Zurich virtual assistant. 🤖 May I help you?
Usecase specific prompts: These prompts can be set on any page where it makes sense to push a particular use case. Example: Page: On the sales page for Trading accounts Prompt: Opening a trading account is as easy as 1, 2, 3...Stuck somewhere? I can help you. Example: Page: On the Technology and Resources Page: These will lead to the Get a chatbot flow Prompt: 🤔 Wondering how our technology can help you? Come, talk to me!
- Some writing tips to keep your prompts interesting:
- Directly address the customer and use “you” to draw their attention.
- Provide a benefit or two.
- Make it relatable and use the user persona as a guide! Call out the emotional value and problem the user may be facing.
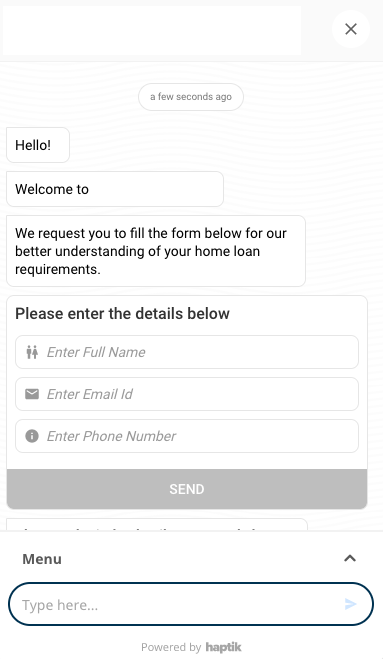
Launch Message
You can use this when you want your users to be greeted with a welcome message by the bot. This also helps to initiate users gently into a conversation.
SmallTalk
SmallTalk is a way to ensure that your bot is able to answer chit chat queries. Since chit chat is usually a conversation starter, it is important to consider SmallTalk while designing your Chat Initiation experience.
- The Haptik platform has a plug-and-play SmallTalk module that allows you to completely edit all SmallTalk steps (around 99 separate intents) and choose your own persona, brand, and content.
- Here’s a 🗝 SmallTalk Module for your perusal. This SmallTalk Module sheet contains all the responses for various user intents based on user persona. You can edit the responses as per your brand communication and guidelines. We have also recommended which of the responses you will require to add the menu items for the user to move ahead in the conversation.
- While you’re editing the SmallTalk module, you will need to make sure to include a menu with menu items as a response for intents like Greetings, Start_Chat, and Capability. This is important because users want to know what the bot can do for them even though they are chitchatting. As a best practice, it is recommended to add some form of re-engagement option to every single intent.
- Here’s the link to the official documentation that covers everything you need to know.
Generic Tips
- Clearly introduce your bot.
- Start with a smile. Not all bots need to be super chatty, hilarious, or whacky but setting a friendly, trustworthy tone at the beginning is important. It tells the user that the bot is meant to solve their issues and not be an annoying machine to prevent human contact.
- Set clear expectations. This will dictate the success of your bot. Tell the user what the bot can do and give them an option if they can’t find their query on the supported list. Ask them to state their query in keywords if that’s what your bot understands best.
- Don’t be bot-centric. Focus on the user instead of focusing on the bot.
Example: When the bot is unable to understand a user’s query, instead of saying, “Oops! I didn’t understand that because I’m a bot”, say “I’m sorry that your query wasn’t resolved. Would you like to start over?”.
